Train-based interventions, doubtlessly serving as both different remedies for melancholy or alongside medicine and/or remedy, are beneficial by the UK Nationwide Institute for Well being and Care Excellence (NICE). Train is a broad time period, and might vary from gradual guided motion akin to yoga, to high-intensity power or cardio coaching, and quite a few scientific trials for melancholy have been performed over the previous a number of many years. Understanding the effectiveness of various kinds of train in treating melancholy, and whether or not particular actions may be higher suited to completely different people, is essential for the event of each interventions and remedy tips.
Earlier Psychological Elf blogs have coated research establishing the effectiveness of exercise as a treatment for depression (Nedoma, 2023), together with a meta-analysis discovering train interventions to be “non-inferior to present first line remedies” (Heisel et al., 2023). As noted by Francesca Bentivega in her 2022 blog, though reductions in melancholy from train interventions are noticed reliably, the mechanisms behind these adjustments are poorly understood, and should effectively differ between people and kinds of train (Bentivegna, 2022).
Of their 2024 evaluation, Noetel and colleagues aimed to establish the best sorts and quantities of train (referring to each the size of intervention and frequency of periods) for treating melancholy, and doable elements that affect who is probably going to answer remedy (referred to as moderators).
Strategies
5 databases have been searched over a two-year interval, figuring out 18,658 papers, with 54 further research recognized from earlier opinions. After preliminary screening, 1,738 research have been assessed for eligibility, with 218 assembly the inclusion standards and included within the evaluation. These inclusion standards have been:
- Randomised managed trials
- Longer than one week in size
- A minimum of one train group
- Individuals met scientific cut-offs for main melancholy
- Melancholy reported as an final result
- Satisfactory knowledge to calculate an impact dimension for every examine arm.
The first evaluation comprised a multilevel community meta-analysis, which in precept permits for a comparability between various kinds of train throughout research, with impact sizes introduced as advantages past ‘energetic management’ circumstances. Management circumstances assorted considerably between research, for instance: traditional care, placebo pill, stretching, academic management, or social help; for the aim of research, the authors mixed these circumstances right into a single ‘energetic management’ group.
Outcomes
The ‘community geometry’ determine from the paper (reproduced beneath) illustrates the variety of individuals in every intervention arm (indicated by the scale of the circles) and the variety of direct comparisons between arms (indicated by the thickness of the strains). It exhibits notable variations within the frequency with which completely different interventions have been investigated, and that completely different train sorts have principally been in contrast with ‘energetic management’; there are only a few direct comparisons between various kinds of train, or with first-line remedies for melancholy (i.e. selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or cognitive behavioural remedy (CBT)).
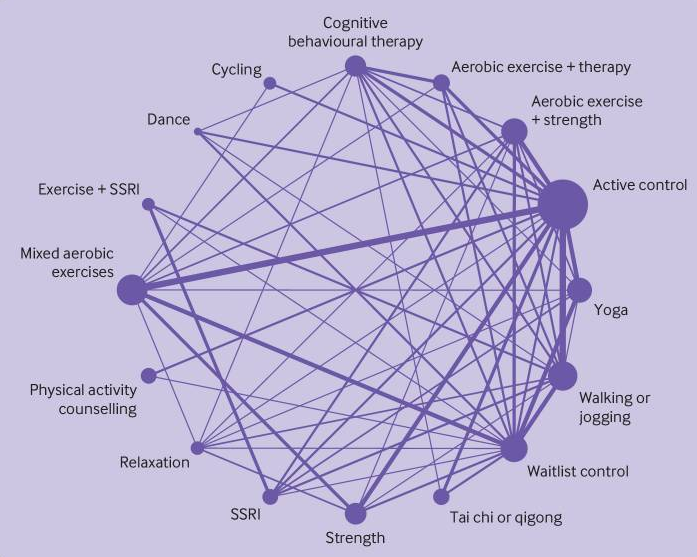
The intervention teams included within the meta-analysis, with the scale of the dots indicating the variety of individuals, and the thickness of the strains indicating the variety of direct comparisons between examine arms. [View full size graphic]
Hedges g scores (within-subject standardised imply variations, referred to as impact sizes) have been calculated for every examine arm individually (i.e., post- versus pre-intervention, the place a extra unfavourable quantity signifies a higher discount in melancholy), and aggregated throughout research inside every intervention class. Every intervention was then in contrast with ‘energetic management’ (summarised beneath).
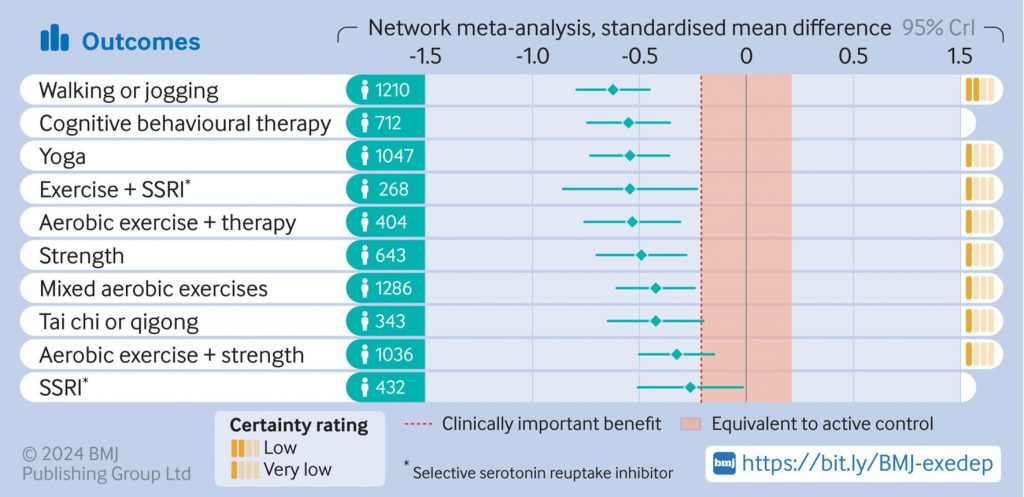
Impact sizes from every intervention in contrast with ‘energetic management’. The yellow bars on the suitable point out credibility rankings, primarily based on each pattern dimension and the authors’ judgment of examine high quality. [View full size graphic]
Conclusions
The principle conclusions of the examine are as follows:
- A number of kinds of train proved efficient as remedies for melancholy, for instance strolling or jogging, yoga, and power coaching, with dancing exhibiting notably robust results (albeit with decrease certainty owing to the small pattern dimension);
- Extra intense train was related to a higher antidepressant impact;
- Advantages seemed to be comparable for various baseline melancholy scores, and comorbidities;
- Age and gender would possibly affect which train sort is more likely to be efficient, though this must be confirmed in research particularly designed to analyze particular person variations.
The authors conclude that remedy tips round train for melancholy might at present be too conservative, and that tailoring train to particular person affected person traits would possibly enhance the probabilities of success.

Present train tips for melancholy could also be too cautious. Personalising train plans to suit every particular person may increase their probabilities of feeling higher.
Strengths and limitations
The rigorous inclusion standards and broad breadth of research screened are essential strengths of the evaluation. Solely randomised managed trials together with individuals who reached scientific cut-offs of melancholy have been analysed, that means we might be assured that the outcomes reported replicate the consequences of interventions on individuals with scientific melancholy.
The applying of community meta-analysis can also be a power, because it doubtlessly permits for the comparability of various kinds of intervention, regardless of the shortage of many direct comparisons inside research. Nonetheless, the kind of “arm-based” community meta-analysis utilized on this examine can also be a weak spot, as in contrast to “contrast-based” evaluation, it doesn’t protect the randomised facet of comparisons inside trials; subsequently, warning have to be utilized when weighing up the effectiveness of various interventions on this method, owing to the oblique nature of the comparisons. This limitation is especially related to the comparisons between various kinds of intervention (e.g., train vs SSRIs), particularly because the authors didn’t really examine any of the completely different interventions statistically. Nonetheless, the outcomes present a helpful illustration of which kinds of train are mostly investigated, what they’ve been in comparison with, and preliminary indications of which of them work finest. This lays the groundwork for future analysis to deal with understudied areas. Equally, the rigour with which the authors assessed the chance of bias and examine high quality permits the identification of weak factors throughout the present literature.
One complication in decoding the outcomes is the usage of a mixed ‘energetic management’ situation, comprising traditional care, placebo pill, stretching, academic management, or social help. For instance, presumably ‘stretching’ has a number of comparable options to ‘yoga’ or ‘tai chi/qigong’, whereas ‘academic management’ may doubtlessly be fairly much like ‘bodily exercise counselling’. These gray areas between the ‘energetic management’ and intervention teams, with the mixed ‘energetic management’ group together with interventions much like these with each clinically essential advantages (e.g., stretching and leisure), and people beneath that threshold (e.g., bodily exercise counselling), may muddy the waters, doubtlessly leading to both under- or over-estimation of impact sizes.
Moreover, as any comparability between interventions throughout the evaluation is essentially oblique (as few research included multiple sort of train), a excessive stage of warning is critical when drawing conclusions. That is notably related for interventions with decrease pattern sizes and few direct comparisons, akin to dance, as estimates of the distinction between interventions will probably be imprecise. Equally, the doable intercourse and age variations recognized by exploratory moderation analyses are very preliminary and require additional investigation, particularly as analyses have been primarily based on the typical gender combine or age in every examine arm, fairly than investigated on the particular person participant stage.
A further and substantial limitation is the small pattern dimension of a lot of the research included within the meta-analysis (on common <30 individuals per arm, and fewer than ten research included >100 individuals), in addition to clear proof for publication bias (this refers to the truth that research reporting important outcomes usually tend to be revealed). This raises the prospect that the outcomes of the meta-analysis will not be correct, as impact sizes for train interventions vs ‘energetic management’ will probably be over-estimated. Nonetheless, it’s price noting that even when analysing solely research that reported a non-significant consequence, the authors nonetheless noticed a big impact when evaluating train (throughout every kind) with ‘energetic management’, albeit unsurprisingly with a a lot smaller impact dimension. To handle this situation, we want giant trials that consider the effectiveness of train interventions, ideally incorporating a number of intervention arms (which might permit for direct comparisons between various kinds of train).
A ultimate limitation is much like the purpose raised within the aforementioned weblog “Aerobic exercise improves symptoms in students with major depression”, which emphasised our lack of know-how relating to the mechanisms by which train improves melancholy. While this examine lays out the proof base supporting the implementation of train as a remedy for melancholy, the mechanisms behind its effectiveness stay unclear – particularly given the big selection actions studied, which presumably may function by completely different mechanisms. Moreover, the kinds of train exhibiting promise assorted significantly when it comes to group/solo format, depth, motion sort, muscle teams used, and cardio/anaerobic calls for, elevating essential questions as to which of those elements are most essential for treating melancholy, and underscoring the significance of mechanistic analysis. Though preliminary proof of mediating elements, akin to vanity, self-efficacy, and social connection exists (White et al., 2024), these elements have primarily been assessed utilizing self-report questionnaires, and the cognitive, neural and physiological mechanisms driving these adjustments are far much less effectively understood. To handle this query, mechanistic randomised managed trials are required, which might contain taking cognitive, neural and physiological measures earlier than, throughout and after train and management interventions, within the context of a randomised design.

All kinds of actions may also help deal with melancholy, starting from yoga and tai chi to high-intensity power and cardio coaching.
Implications for follow
Though bodily exercise is beneficial by the World Well being Organisation (WHO) and included within the UK NICE tips for melancholy, arguably it’s not ‘prescribed’ at a frequency commensurate with its supporting proof base. Along with summarising the present literature supporting the usage of train interventions for melancholy, this paper supplies preliminary proof for the potential utility of tailor-made train suggestions primarily based on particular person traits, in addition to suggesting that extra intense train is more likely to be simpler.
Retaining train in thoughts as a viable remedy choice for melancholy is advisable, and emphasising its potential not simply as a substitute, but additionally doubtlessly as an addition to first-line remedies, could also be essential to encourage extra uptake. Neighborhood-based exercise lessons particularly designed for individuals with melancholy are extraordinarily unusual within the UK, subsequently growing funding for exercise-based interventions inside psychological well being or major care companies may result in higher consciousness and scale back present limitations to each prescription and attendance.
Importantly, few research within the meta-analysis obtained follow-up knowledge for greater than three months, and subsequently the longer-term affect of train on melancholy stays unsure – even when train is efficient, it’s probably that if people cease exercising then the chance of relapse will probably be excessive. Subsequently, a key aim when it comes to implementation in companies ought to be to encourage individuals to keep up an train routine in the long term, after the tip of a programme of lessons. For instance, this may be achieved by designing interventions that may be carried out extra virtually into individuals’s lives, and routines such because the idea of train ‘snacks’ (Thøgersen-Ntoumani et al 2024).
One other method of facilitating a cultural shift in direction of higher use of train in psychological well being settings is thru understanding the mechanisms driving optimistic change. For instance, the LIFE Trial at present going down at College Faculty London (UCL), is investigating the organic, neural, and psychological processes modified by train in melancholy. If such analysis does yield improved mechanistic understanding, it couldn’t solely enhance affected person and healthcare professionals’ willingness to think about it, but additionally present additional indications as to how train interventions might be tailor-made to people.

Regardless of being included in NICE and WHO tips, train is just not ‘prescribed’ sufficient for individuals with melancholy.
Assertion of pursuits
The authors are a part of the examine crew of the LIFE Trial talked about within the ‘Implications for Follow’ part, however in any other case declare no conflicts of curiosity.
Acknowledgements
Honest due to the remainder of the UCL LIFE examine crew (Prof Glyn Lewis, Prof Mark Hamer, Dr. Emily Hird, Dr. Elle Newton, Ashley Slanina-Davies, Jehanita Jesuthasan) for his or her feedback and suggestions that helped form this weblog, to Prof Deborah Caldwell for kindly answering a number of statistical queries, and to Dr Michael Noetel, the primary creator of the mentioned paper, for his well timed and detailed responses to our enquiries in the course of the writing course of.
Hyperlinks
Main paper
Noetel M, Sanders T, Gallardo-Gómez D, Taylor P, Del Pozo Cruz B, van den Hoek D, Smith JJ, Mahoney J, Spathis J, Moresi M, Pagano R, Pagano L, Vasconcellos R, Arnott H, Varley B, Parker P, Biddle S, Lonsdale C. (2024) Effect of exercise for depression: systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials – PubMed. British Medical Journal 2024, 384 q1024.
Different references
Francesca Bentivegna (2022) Cardio train for main melancholy: the function of reward processing and cognitive management. https://www.nationalelfservice.net/treatment/exercise/aerobic-exercise-major-depression/
Ross Nedoma (2023) Train for melancholy: an evidence-based remedy choice. https://www.nationalelfservice.net/treatment/exercise/exercise-for-depression-an-evidence-based-treatment-option/
Heissel, A., Heinen, D., Brokmeier, L. L., Skarabis, N., Kangas, M., Vancampfort, D., Stubbs, B., Firth, J., Ward, P. B., Rosenbaum, S., Hallgren, M., Schuch, F. (2023). Exercise as medicine for depressive symptoms? A systematic review and meta-analysis with meta-regression. British Journal of Sports activities Drugs 2023 57 1049-1057.
Thøgersen-Ntoumani, C., Grunseit, A., Holtermann, A., Steiner, S., Tudor-Locke, C., Koster, A., Johnson, N., Maher, C., Ahmadi, M., Chau, J. Y., & Stamatakis, E. (2024). Promoting vigorous intermittent lifestyle physical activity (vilpa) in middle-aged adults: an evaluation of the movsnax mobile app. BMC public well being, 2024 24(1) 2182.
White, R. L., Vella, S., Biddle, S., Sutcliffe, J., Guagliano, J. M., Uddin, R., Burgin, A., Apostolopoulos, M., Nguyen, T., Younger, C., Taylor, N., Lilley, S., Teychenne, M. (2024). Physical activity and mental health: a systematic review and best evidence synthesis of mediation and moderation studies. Worldwide Journal of Behavioural Diet and Bodily Exercise, 2024 21(134)

