Stopping depressive relapse is a significant purpose within the administration of bipolar dysfunction. It has been proven that melancholy makes up round 72% of general time spent ailing in individuals with bipolar (Forte et al., 2015), and that bipolar melancholy particularly is related to vital bodily and psychological morbidity, in addition to elevated mortality (Baldessarini et al., 2020).
Lithium is the first-line really helpful treatment for stopping bipolar melancholy (NICE, 2014). Nonetheless, as a earlier Elf blog has highlighted, prescription of lithium is declining, each within the UK and different international locations (Edward, 2019). Antipsychotics, different temper stabilisers and – though not really helpful by NICE – antidepressants are additionally usually prescribed long-term for individuals with bipolar dysfunction. As not too long ago blogged here and here, using antidepressants within the long-term administration of bipolar dysfunction is controversial, with the chance of temper destabilisation related to antidepressant monotherapy, and it is suggested that they need to be prescribed for sufferers with bipolar dysfunction solely in particular medical eventualities (McIntyre et al., 2020; Pacchiarotti et al., 2013).
In a paper not too long ago printed in The Lancet Psychiatry, Ermis et al (2025) aimed to check whether or not the prescription of medicines utilized in bipolar melancholy have an effect on the probabilities of sufferers with bipolar dysfunction being admitted to hospital because of a depressive temper episode.

Stopping depressive relapse is a significant purpose within the administration of bipolar dysfunction.
Strategies
Ermis et al used a cohort examine design to establish whether or not prescription of temper stabilisers, antidepressants and antipsychotics have been related to admission to hospital resulting from depressive sickness (major consequence), and admission to hospital resulting from mania or a somatic situation (secondary outcomes). Topics and consequence knowledge have been recognized from ICD-10 codes (WHO, 2019) in Swedish nationwide registers from 2006-2021, while knowledge on topics’ medicines have been gathered from the Prescribed Medicine Register.
A within-subjects Cox regression evaluation (adjusted for time-variant covariates akin to time since cohort entry and use of different psychopharmacological medicines) was used to match durations of time through which the topic was prescribed a selected treatment towards instances through which no antidepressant, antipsychotic, or temper stabiliser have been prescribed. Various sensitivity analyses have been additionally performed, to make sure the robustness of the findings.
Outcomes
105,495 individuals with bipolar dysfunction have been included. The imply age of the pattern was 44.2 years (normal deviation, SD 18.8), and 62.2% of the pattern recognized as ladies. Comorbidities have been current in a big minority (nervousness issues 40.5%, substance use dysfunction 18.8%, character issues 10.4% and former suicide try 10.6%).
Comply with-up was commenced from the date of bipolar prognosis and the imply follow-up time was 9.1 years (SD 5.1). At follow-up, antidepressant monotherapy was the commonest publicity (utilized by 59,963 topics, 56.8% of the cohort, in some unspecified time in the future through the follow-up interval), adopted by temper stabiliser monotherapy (47,931, 45.4%) and antidepressant-mood stabiliser mixture (46,318, 43.9%).
General, 16,190 topics (15.3%) have been hospitalised with a depressive episode not less than as soon as through the follow-up interval; 8,066 topics (7.7%) have been hospitalised resulting from mania.
Decreased likelihood of depression-related hospitalisation
- Temper stabiliser monotherapy was the one treatment group discovered to be related to a decreased likelihood of depression-related hospitalisation in contrast with the prescription of no medicines in any respect (adjusted hazards ration, aHR 0.89, 95% confidence interval, CI 0.81 to 0.98).
- Temper stabilisers mixed with antipsychotics have been related to a slightly decreased likelihood of depression-related hospitalisation, however this was not statistically vital (aHR 0.92, 95% CI 0.85 to 1.00).
- In particular person treatment evaluation, solely lithium was related to a decreased likelihood of admission resulting from melancholy on this cohort of individuals with bipolar dysfunction (aHR 0.75, 95% CI 0.67 to 0.85).
Elevated likelihood of depression-related hospitalisation
- Aside from temper stabiliser monotherapy and temper stabilisers mixed with antipsychotics, all different treatment teams, both alone or together, have been discovered to be related to an elevated likelihood of depression-related hospitalisation.
- Notably, a number of medicines have been related to an elevated likelihood depression-related hospitalisation, specifically quetiapine, duloxetine, citalopram, olanzapine, mirtazapine, vortioxetine and aripiprazole.
Decreased likelihood of hospitalisation resulting from a somatic situation
- When it comes to secondary outcomes, lithium was the one treatment related to a decreased likelihood of hospitalisation resulting from a somatic situation (aHR 0.86, 95% CI 0.80 to 0.93), with no statistically vital associations being discovered between the opposite medicines and somatic hospitalisation.
Elevated likelihood of mania-related hospitalisation
- Antidepressants-only have been the one group that have been related to elevated probabilities of hospitalisation resulting from mania (aHR 1.22, 95% CI 1.03 to 1.44); all different medicines teams, alone or together, have been related to decreased probabilities of mania-related hospitalisation.
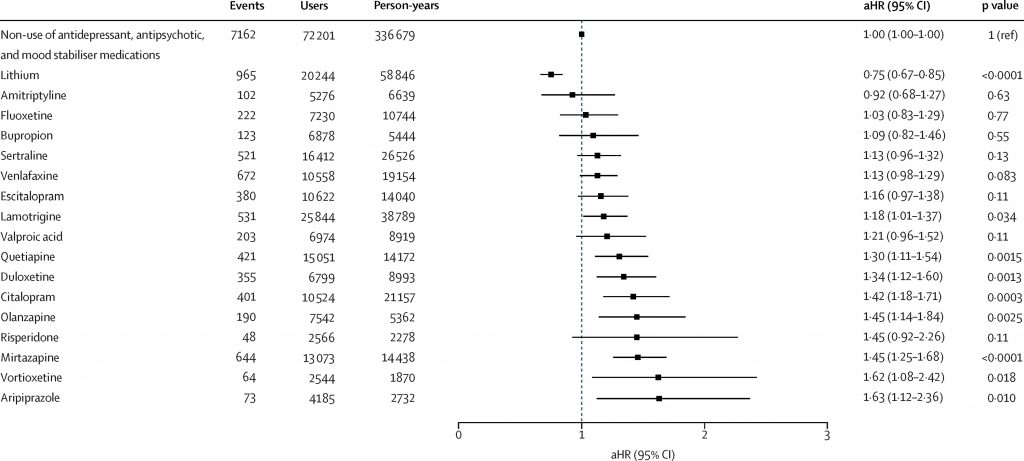
In particular person treatment evaluation, solely lithium confirmed a decreased likelihood of depression-related hospitalisation; all different medicines have been both equivocal or related to elevated likelihood of depression-related hospitalisation. [View full sized graphic]
Conclusions
The outcomes of this examine spotlight that lithium is the one monotherapy that decreases the probabilities of depression-related hospitalisation in individuals with bipolar dysfunction. Extra advantages have been additionally seen within the probabilities of mania-related and somatic hospitalisations, emphasising lithium’s multimodal advantages.
In distinction, sure antidepressants and antipsychotics have been related to elevated likelihood of depression-related hospitalisation.
“Present findings supported the notion that lithium ought to stay the mainstay of remedy in bipolar dysfunction” – Ermis et al, 2025
Strengths and limitations
A cohort examine design was the best methodology to reply this query. Cohort research, of their observational nature, permit researchers to establish the impact of exposures in pure environments, making the outcomes extra generalisable to real-life conditions. It additionally allowed the authors to match a number of medicines on the identical time, which might not have been attainable to the identical extent in, for instance, an RCT design.
The examine inhabitants was taken from Swedish nationwide registers and ICD-10 codes have been used to determine these with bipolar dysfunction and the outcomes of curiosity. The outcomes are subsequently reliant on right software of the ICD-10 standards at time of prognosis and proper coding of prognosis into the well being registers. Inside these limitations, the authors have been in a position to pattern a lot of the inhabitants with a bipolar prognosis and supply follow-up over a number of years.
When it comes to the pattern demographics, charges of psychiatric comorbidity and suicide try historical past have been excessive, however this echoes the broader bipolar inhabitants (as highlighted by a previous Elf blog) and improves the generalisability of the outcomes from this pattern to real-world medical settings. It’s notable, nonetheless, that there have been twice as many ladies than males, which isn’t reflective of bipolar dysfunction’s 1:1 male-to-female distribution and that knowledge on ethnicity weren’t out there, each of which restrict the generalisability of the examine outcomes to specific teams.
The authors famous that by specializing in hospitalisation, the outcomes of this examine are solely related for essentially the most extreme circumstances of bipolar melancholy and don’t take into account the advantages or harms that these medicines could also be exerting in sufferers who’re managed totally as outpatients. Hospitalisation is an goal, binary measure that has vital real-world implications for sufferers, and so it may be argued that it’s nonetheless measure of the efficacy of those medicines.
A ultimate vital consideration is that use of registry knowledge doesn’t all the time correspond precisely to behavior. In different phrases, simply because a prescription was written, doesn’t imply the treatment was taken. Usually talking, nonetheless, it’s possible that almost all of these prescribed a medicine do take it, and the big numbers included on this pattern are prone to minimise the impact that treatment non-compliance in small minority could have on general outcomes.

Regardless of limitations, the big pattern measurement and lengthy follow-up make the outcomes pretty generalisable to the bipolar inhabitants and vital medical eventualities.
Implications for apply
This paper reaffirms the standing of lithium as “the simplest long-term remedy for bipolar dysfunction” (NICE, 2014). As such, it’s regarding that the charges of lithium prescription look like declining (Lyall et al., 2019). The explanations for this are unclear, however, as a earlier Elf blog highlights, it might be resulting from nervousness amongst sufferers and clinicians in regards to the elevated monitoring that’s required for lithium or resulting from its particular opposed impact profile. It might even be associated to the low value of lithium, which can be driving the pharmaceutical business to promote using different, dearer choices, doubtlessly swaying affected person choice. Regardless of the purpose, a transfer away from prescribing lithium poses the chance of many sufferers lacking out on its potential advantages.
After lithium, the second- and third-line NICE-recommended preventative medicines for bipolar dysfunction are antipsychotic monotherapy and augmentation with valproate. This paper confirmed that these medicines have been related to reductions in mania-related hospitalisation, however no such profit was seen with depression-related hospitalisation. Some antipsychotics have been in reality related to elevated likelihood hospitalisation resulting from a depressive episode. This may occasionally make clinicians assume twice about prescribing antipsychotics or valproate long-term in bipolar dysfunction if the first intention of remedy is to stop additional depressive moderately than manic relapses. In lots of sufferers this would be the intention, notably as melancholy makes up the vast majority of sickness time in these with bipolar dysfunction (Forte et al., 2015).
So, on the very least, Ermis et al have demonstrated the necessity for additional analysis on this space in order that we are able to make clear whether or not present medical pointers for prevention of bipolar relapse are match for objective for every type of temper episodes, particularly in these for whom lithium will not be an choice.

A transfer away from prescribing lithium poses the chance of many sufferers lacking out on its potential advantages.
Assertion of pursuits
No conflicts of curiosity to declare.
I’m at present in receipt of PhD fellowship funding by a Wellcome Belief-funded examine in bipolar dysfunction, sleep and circadian rhythm (www.ambientbd.com).
Hyperlinks
Major paper
Ermis, C., Taipale, H., Tanskanen, A., Vieta, E., Correll, C. U., Mittendorfer-Rutz, E., & Tiihonen, J. (2025). Real-world effectiveness of pharmacological maintenance treatment of bipolar depression: a within-subject analysis in a Swedish nationwide cohort. The Lancet Psychiatry.
Different references
Alsaif, M. (2017). Antidepressants for bipolar melancholy. Nationwide Elf Service. https://www.nationalelfservice.net/mental-health/bipolar-disorder/antidepressants-for-bipolar-depression/
Baldessarini, R. J., Vázquez, G. H., & Tondo, L. (2020). Bipolar melancholy: a significant unsolved problem. Worldwide journal of bipolar issues, 8(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40345-019-0160-1
Edward, D., & Ahmed, S. (2019, 14 June 2019). Prescribing lithium for bipolar dysfunction: are we too scared? The Psychological Elf. https://www.nationalelfservice.net/mental-health/bipolar-disorder/prescribing-lithium-bipolar-disorder/
Forte, A., Baldessarini, R. J., Tondo, L., Vázquez, G. H., Pompili, M., & Girardi, P. (2015). Lengthy-term morbidity in bipolar-I, bipolar-II, and unipolar main depressive issues. J Have an effect on Disord, 178, 71-78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2015.02.011
Kalfas, M. & Leeks, P. (2024). Jury stays out on antidepressant-induced mania. Nationwide Elf Service. https://www.nationalelfservice.web/mental-health/bipolar-disorder/antidepressant-induced-mania/
Lyall, L. M., Penades, N., & Smith, D. J. (2019). Modifications in prescribing for bipolar dysfunction between 2009 and 2016: national-level knowledge linkage examine in Scotland. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 215(1), 415-421. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.2019.16
McIntyre, R. S., Berk, M., Brietzke, E., Goldstein, B. I., López-Jaramillo, C., Kessing, L. V., Malhi, G. S., Nierenberg, A. A., Rosenblat, J. D., & Majeed, A. (2020). Bipolar issues. The Lancet, 396(10265), 1841-1856. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31544-0
NICE. (2014). Suggestions | Bipolar dysfunction: Evaluation and Administration | Steerage | NICE. Nationwide Institute for Well being and Care Excellence. https://www.good.org.uk/steerage/cg185
Pacchiarotti, I., Bond, D. J., Baldessarini, R. J., Nolen, W. A., Grunze, H., Licht, R. W., Publish, R. M., Berk, M., Goodwin, G. M., & Sachs, G. S. (2013). The Worldwide Society for Bipolar Problems (ISBD) activity power report on antidepressant use in bipolar issues. American Journal of Psychiatry, 170(11), 1249-1262. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.2013.13020185
Pell, C. (2013). Summing up suicide knowledge in bipolar dysfunction. The Psychological Elf. https://www.nationalelfservice.web/mental-health/bipolar-disorder/summing-up-suicide-data-in-bipolar-disorder/
WHO. (2019). ICD-10 Model:2019. World Well being Organisation. https://icd.who.int/browse10/2019/en