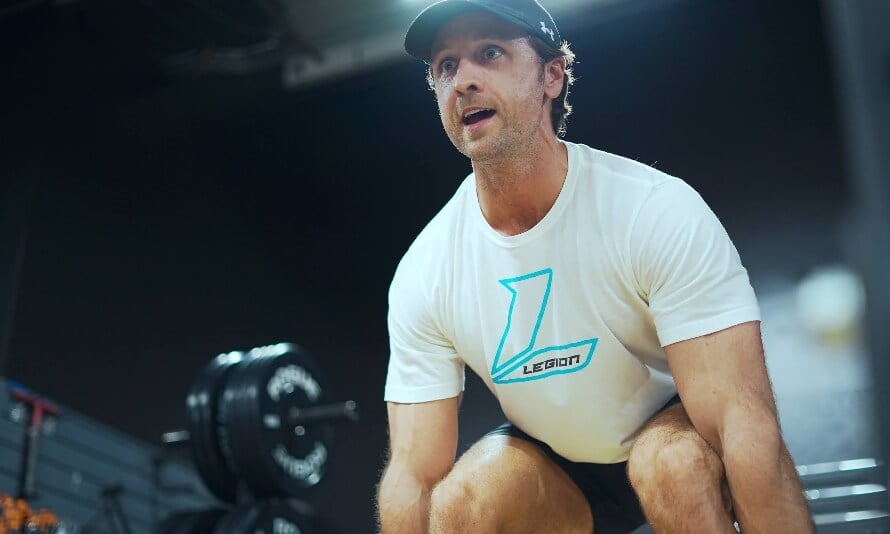
Most deadlifters know the frustration of pulling with all of your may, solely to have the bar stubbornly keep on the ground.
If that sounds acquainted, there’s an train you want to attempt: the deficit deadlift.
By rising the vary of movement, the deficit deadlift helps you construct explosive energy from the bottom up, boosting your total deadlift efficiency. Plus, it’s incredible for including mass to your legs and again, lowering your threat of harm, and even bettering athletic efficiency.
On this article, you’ll study precisely the best way to do the deficit deadlift, perceive why it’s so efficient, discover the perfect alternate options, and extra.
Key Takeaways
- A deficit deadlift is a deadlift variation the place you stand on an elevated floor to extend the vary of movement.
- The principle advantages of deadlifting with a deficit are that it enhances common deadlift power, boosts athletic efficiency, and should shield in opposition to hamstring and ACL harm.
- Deficit variations of the sumo, Romanian, and stiff-leg deadlift are viable alternate options to the common deficit deadlift in case your flexibility permits you to carry out them accurately.
- The deficit deadlift trains your total decrease physique and again.
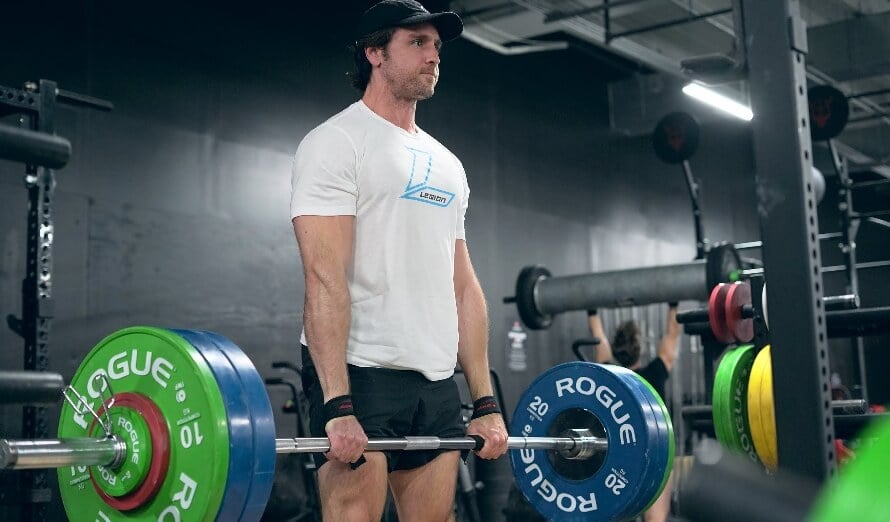

What Is the Deficit Deadlift?
A deficit deadlift is a variation of the conventional deadlift the place you stand on an elevated floor, like a weight plate or platform, to extend the vary of movement.
Right here’s the way it seems to be:


You may also hear it referred to as the “elevated deadlift” or “raised deadlift,” however these phrases consult with the identical train.
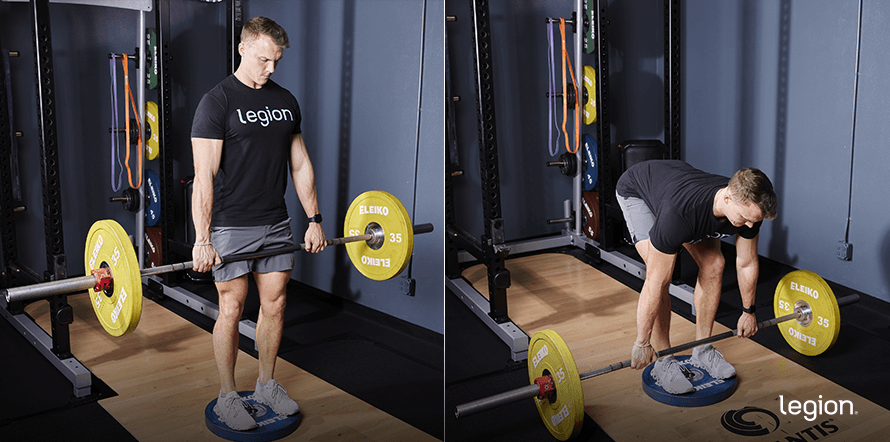
Find out how to Do the Deficit Deadlift
To learn to deficit deadlift, break up the train into three components: arrange, pull, and descend.
1. Arrange
Earlier than you deal with the deficit deadlift, you want to set the suitable deficit top. Discovering the proper deficit top in your proportions can take some experimenting.
As a common rule, a 2-inch deficit is an efficient place to begin, although for those who’re versatile or have lengthy arms, a 3-inch deficit could be extra becoming.
To create the deficit, you need to use any sturdy floor elevated 2-to-3 inches off the ground. Whereas there are specialised deficit deadlift platforms and blocks for this goal, most weightlifters make do with a weight plate or a powerful step.
Assuming you’re utilizing a weight plate, right here’s what to do: Place the burden plate on the ground, stand on it with a hip-width stance, and level your toes barely outward. Roll a loaded barbell over your midfoot, positioning it about an inch out of your shins.
Bend over and seize the bar along with your palms dealing with you, simply exterior your shins. Take a deep breath to fill your stomach with air, and brace your abs such as you’re about to take a punch.
Push your hips as much as flatten your again, and wedge your self right into a “half-squat” place. Pull your shoulder blades again and down, and squeeze your higher arms into your sides (think about you’re crushing oranges in your armpits).
2. Pull
Squeeze the bar as onerous as you may and pull it straight up.
Your hips and shoulders ought to rise concurrently—don’t shoot your hips up after which use your again like a lever to lift your shoulders.
As soon as the bar passes your knees, push your hips into the bar. On the prime of the rep, push your chest up and your shoulders down, however don’t lean again, hyperextend your decrease again, or shrug the burden.
3. Descend
Whereas holding your again flat and your core tight, reverse the motion to return the bar to its beginning place on the ground.
Don’t attempt to decrease the bar slowly or quietly. The complete descent ought to take a couple of second. Take a second to get within the correct beginning place, then begin your subsequent rep.
Right here’s the way it ought to look while you put all of it collectively:


Deficit Deadlift Advantages
Enhanced Deadlift Efficiency
Pulling the bar off the ground is the toughest a part of the deadlift for many weightlifters. Performing deadlifts with a deficit forces your muscular tissues to work tougher by way of this weak vary of movement, improving your efficiency while you return to standard deadlifting.
Decreased Damage Danger
Muscle imbalances between the quadriceps and hamstrings are a major cause of decrease physique accidents, particularly to the hamstrings and ACL. Deficit deadlifts strengthen the hamstrings, which many individuals neglect. This helps appropriate power imbalances, doubtlessly reducing your threat of harm.
Improved Athletic Efficiency
The deficit deadlift trains many main muscle teams all through the physique, particularly, the glutes, hamstrings, quads, and back. Strengthening these muscular tissues permits them to generate extra power, which boosts your potential to carry out athletic actions like sprints and jumps.
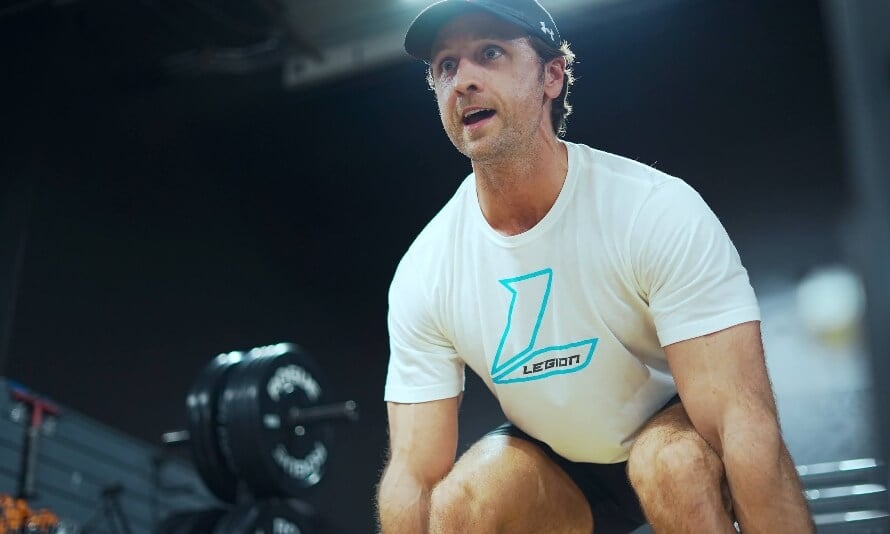


The Finest Deficit Deadlift Variations
1. Deficit Sumo Deadlift
The sumo deficit deadlift works the identical muscular tissues because the common deficit deadlift however emphasizes the quads extra and the lower back much less. It’s a fantastic various if the usual model bothers a pre-existing again problem. Simply bear in mind, it requires extra hip mobility, so it won’t be excellent when you have restricted flexibility.
RELATED: The Definitive Guide to the Sumo Deadlift
2. Deficit Romanian Deadlift
The deficit Romanian deadlift stretches your hamstrings greater than the common model, which research reveals might help development. That mentioned, it additionally requires considerably extra flexibility, so it is probably not appropriate for everybody.
RELATED: How to Do the Romanian Deadlift: Form, Benefits, and Variations
3. Deficit Stiff-Leg Deadlift
The deficit stiff-leg deadlift is nearly the identical because the deficit Romanian deadlift, besides you retain your legs straighter and decrease the bar to the ground on the finish of every rep. Each workout routines successfully train your glutes, hamstrings, and decrease again, however the stiff-leg model is tougher to study and might be uncomfortable. That’s why I normally want and suggest the deficit Romanian deadlift.
RELATED: How to Do Stiff-Leg Deadlifts: Form, Muscles Worked & More
FAQ #1: Are deficit deadlifts tougher?
Sure, deficit deadlifts are tougher than common deadlifts as a result of they’ve a bigger vary of movement. Additionally they power your muscular tissues to work extra on the backside of every rep, which is normally the a part of the motion the place you’re weakest.
FAQ #2: Are deficit deadlifts good?
Sure, deficit deadlifts are wonderful for constructing muscle in your posterior chain (the muscular tissues on the again of your physique) and bettering your deadlift power. Additionally they assist repair weak factors that may result in harm and increase athletic efficiency.
FAQ #3: What does the deficit deadlift work?
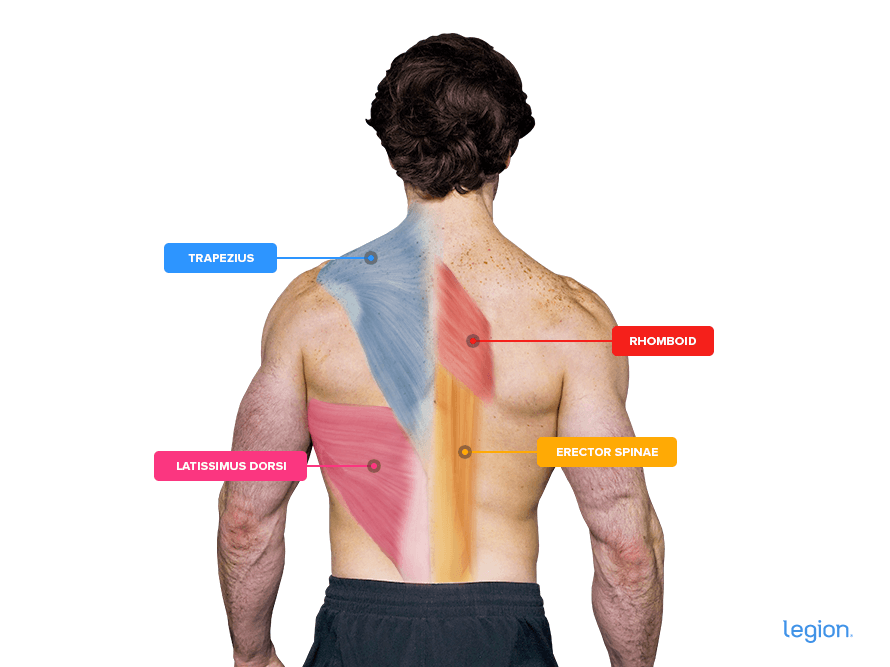
The principle muscular tissues labored by the deficit deadlift are:
- Latissimus dorsi (lats)
- Trapezius (traps)
- Rhomoids
- Spinal erectors (decrease again)
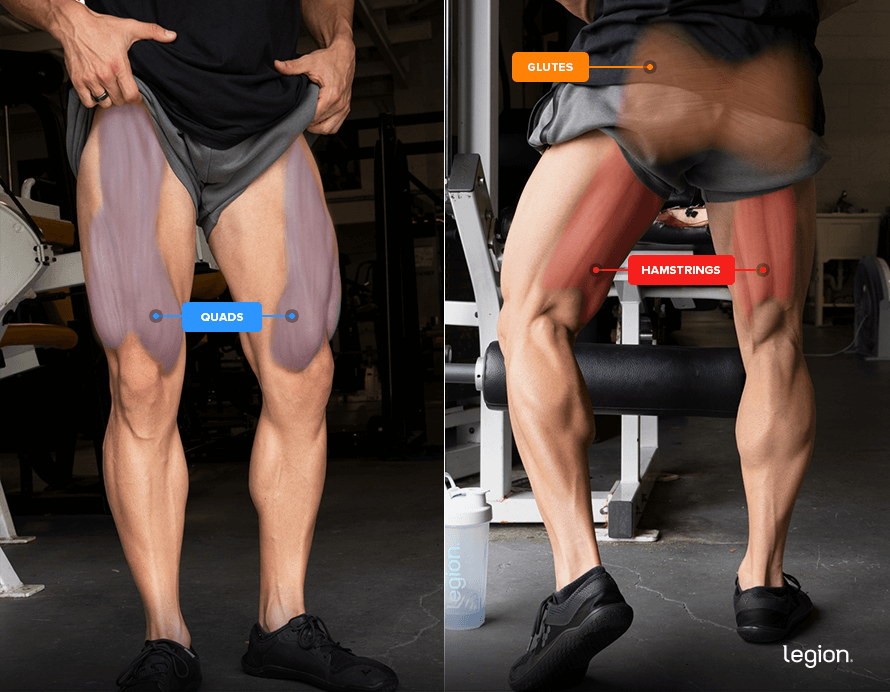
- Glutes
- Hamstrings
- Quadriceps (quads)
- Core
Right here’s how these higher physique muscular tissues look (minus the core):

And right here’s how the decrease physique muscular tissues look:

RELATED: What Muscles Do Deadlifts Work? An Answer, According to Science
Scientific References +
- K. Beckham, George, et al. “Isometric Strength of Powerlifters in Key Positions of the Conventional Deadlift.” Journal of Trainology, vol. 1, no. 2, 2012, pp. 32–35, https://doi.org/10.17338/trainology.1.2_32. Accessed 18 Apr. 2019.
- Kompf, Justin, and Ognjen Arandjelović. “Understanding and Overcoming the Sticking Point in Resistance Exercise.” Sports Medicine, vol. 46, no. 6, 12 Jan. 2016, pp. 751–762, https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-015-0460-2. Accessed 6 Dec. 2019.
- Holcomb, William R., et al. “Effect of Hamstring-Emphasized Resistance Training on Hamstring:Quadriceps Strength Ratios.” The Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, vol. 21, no. 1, 2007, p. 41, https://doi.org/10.1519/r-18795.1.
- Begalle, Rebecca L., et al. “Quadriceps and Hamstrings Coactivation during Common Therapeutic Exercises.” Journal of Athletic Training, vol. 47, no. 4, July 2012, pp. 396–405, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3396299/, https://doi.org/10.4085/1062-6050-47.4.01.
- Seitz, Laurent B., et al. “Increases in Lower-Body Strength Transfer Positively to Sprint Performance: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis.” Sports Medicine, vol. 44, no. 12, 25 July 2014, pp. 1693–1702.
- Thompson, Brennan J, et al. “Barbell Deadlift Training Increases the Rate of Torque Development and Vertical Jump Performance in Novices.” Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, vol. 29, no. 1, 2015, pp. 1–10, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25226322, https://doi.org/10.1519/JSC.0000000000000691.
- Boone, Tommy, et al. Journal of Exercise Physiologyonline Editor-In-Chief JEPonline Electromyographic Activity of Lower Body Muscles during the Deadlift and Still-Legged Deadlift. Vol. 16, no. 3, 2013, www.asep.org/asep/asep/JEPonlineJUNE2013_Miranda.pdf.
